THE STRUCTURE OF THE TOKYO METROPOLITAN GOVERNMENT (TMG)
Organizational Structure of TMG
Tokyo Metropolitan Assembly
Composition
The Tokyo Metropolitan Assembly is made up of 127 members directly elected by Tokyo citizens to serve a term of four years.
The President
The President of the Assembly is elected from among its members. The President represents the Assembly, presides over its sessions, and supervises its affairs. He or she also expresses the Assembly’s opinions externally. As a support organization for the Assembly, a Secretariat is provided and the President is empowered to appoint and dismiss its staff members.
Committees
Because the structure and roles of the metropolitan administration are vast, varied, and complex, in order to ensure thorough discussion and efficient proceedings, the Assembly establishes committees for specialized study and discussion. The committees are divided into standing committees and special committees set up by the Assembly to consider specific subjects.
Authority of the Assembly

The Tokyo Metropolitan Assembly is the formal decision-making organ of Tokyo Metropolis. It has the authority to, among other things, enact, amend, and repeal metropolitan ordinances, approve the budget and certify its settlement, and elect members of the Election Administration Commission and other such bodies. In addition, the consent of the Assembly must be sought for important appointments, nominations, and other designations made by the Governor such as those of a Vice Governor or administrative commission member. Representing the people of Tokyo, the Assembly also has the powers to investigate and inspect all aspects of the metropolitan government.
Executive Organs
The Governor
The Governor is directly elected by the citizens, and represents the Metropolis of Tokyo. With a four-year term of office, he or she has overall control of metropolitan affairs, and the authority and responsibility for managing the metropolitan administration.
Auxiliary Administrative Agencies
To assist the Governor in dealing with the affairs within his authority, Vice Governors and other staff members are provided. A total of 166,079 positions have been approved as of August 1, 2015, for staff members of these auxiliary administrative agencies. (Breakdown: Governor’s bureaus, 24,053; administrative commissions and the Assembly, 993; public enterprises, 12,898; police/firefighting, 64,513; school teachers and administrative staff, 63,622.)
Personnel
Recruitment
The Personnel Commission usually holds examinations for the recruitment of new staff, and candidates who pass the examinations are employed by the Governor and other officials who have appointive powers. In some occupations like nursing, specially authorized officials directly conduct exams and employ personnel.
Recruitment examinations are conducted after being publicly announced to ensure wide public awareness, and they include written examinations and interviews. These examinations are split into different levels according to the difficulty of the questions. The examinations are completely open to everyone on an equal basis regardless of gender, academic background, or social position.
Nationality requirements on about 70% of all positions have been removed, opening up employment opportunities to foreign nationals. To accelerate the employment of disabled persons, examinations are held in braille or using enlarged print, and special selection of people with physical impairments is conducted.
Appointment
The Tokyo Metropolitan Government’s personnel appointment system is based on ability and job performance. Through a fair and impartial selection process, promotion to deputy director and managerial positions is based on personal efforts and merit, rather than academic background or the category an individual was originally hired under.
According to individual career aspirations, “generalization” or “specialization” can be chosen, resulting in a variety of paths for promotion. Young senior staff members are eligible to take the “Managerial Position Selection A” test, and if selected, they are trained to assume managerial positions requiring a metropolitan administration-wide perspective. Team leaders and deputy directors are eligible to take the “Managerial Position Selection B” test, which selects personnel based on their experience and achievements for managerial positions centering on their area of specialty. There is also a selection process for specialists to take on managerial positions in specific areas.
Human Resource Development
In order to respond to the increasingly sophisticated and complex needs of Tokyo residents for administrative services, as well as to develop human resources possessing a high level of knowledge, ability, and experience who can cope with the various challenges Tokyo faces, the metropolitan government has drawn up a set of basic guidelines aimed at developing metropolitan government personnel. Under these guidelines, efforts are taken to manage personnel with a focus on human resource development; this includes training, performance evaluation, and deployment of personnel resources.
The basic approach taken with respect to solid employee training is to shape individual staff capabilities to match organization needs, and to respond to employee motivation for skill improvement, developing individual capabilities to the fullest. From this perspective, the metropolitan government is implementing a practical and comprehensive human resource development program that effectively combines (1) on-the-job training through daily duties in the workplace, (2) off-the-job training undertaken away from daily duties, and (3) personal development through self-education.
Organization of the TMG (as of April 1, 2016)
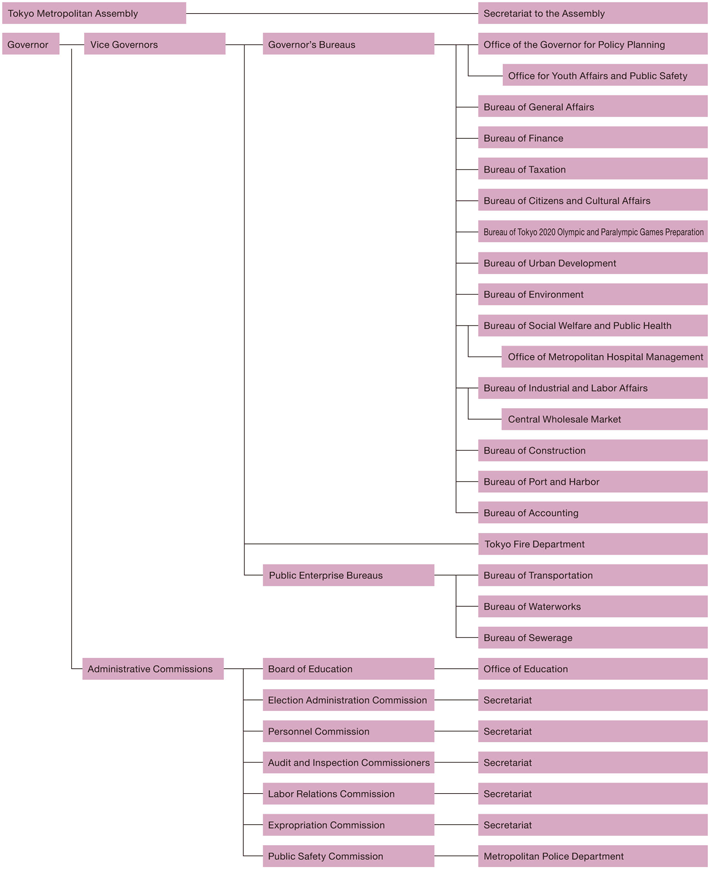
Operations
Governor's Bureaus
Office of the Governor for Policy Planning
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Coordination Division
- Planning Division
- International Affairs Division
Principal operations
Assists the top management operations of the governor including:
- Overalll coordination of important policies
- Planning and proposal of important policies under the special order of the governor
- Liaison with the press
- Cooperation with the central government and neighboring local governments
- Arrangement of a business environment by leveraging the Special Zone system
- Formulation of comprehensive long-term plans
- Promotion of city dipomacy
Office for Youth Affairs and Public Safety
Bureau/Division
- Youth Affairs and Public Safety Division
Principal operations
Cooperates widely with related organizations in order to realize a safe society and to support the sound development and independence of youth through implementation of integrated and comprehensive policies for:
- Youth affairs
- Public safety
- Traffic safety
Bureau of General Affairs
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Disaster Recovery Support Division
- Administrative Reform Promotion Division
- Information and Communications Planning Division
- Tokyo Metropolitan University Support Division
- Personnel Division
- Administrative Inspection Office
- Local Administration Division
- Disaster Prevention Division
- Statistics Division
- Human Rights Division
Principal operations
Coordinates and promotes projects and policies that straddle various bureaus to ensure the smooth implementation of work of the TMG as a whole:
- Internal management work such as administrative reform, advancing information technology, controlling organizations and budgeted number of staff and their appointment and dismissal, labor management, and staff welfare
- Implementation of matters requiring a unified approach such as law interpretation, ordinance proposals, and litigations
- Disaster reduction and crisis management
- Human rights policies
- Support to regions affected by the Great East Japan Earthquake of 2011 as well as to their displaced citizens residing in Tokyo
Others:
- Provision of advice and coordination with municipalities for administrative and fiscal management
- Compilation of statistics
- Support for management of the Tokyo Metropolitan University
Bureau of Finance
Bureau/Division
- Accounting Division
- Budget Division
- Property Administration Division
- Public Building Construction and Maintenance Division
Principal operations
Responsible for the budget and other fiscal affairs and undertakes work on:
- Formation of the budget
- Formulation of mid- and long-term fiscal plans
- Overall management of contracts
- Operation and management of TMG-owned vehicles
- Overall coordination and use of TMG properties
- Design and construction of TMG-owned structures
- Provision of technical support to the other bureaus for maintenance work
- Management, operation, maintenance and other work concerning the TMG building and related facilities
Bureau of Taxation
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Tax System Division
- Taxation Division
- Property Tax Division
- Tax Collection Division
Principal operations
Responsible for:
- Imposition and collection of a total of 16 categories of metropolitan taxes that are the foundation of Tokyo’s finances, including business tax, motor vehicle tax, gas oil delivery tax, real estate acquisition tax, and fixed assets tax (for the 23 special wards only)
- Planning and coordination of tax systems for each category
- Response to tax inquiries by Tokyo residents
- Tokyo Metropolitan Taxation offices and branch offices located throughout the wards and Tama area
- Tokyo Metropolitan Tax Operations Center
- Automobile taxation offices
Facilities include:
Bureau of Citizens and Cultural Affairs
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Public Relations and Public Hearings Division
- Citizens’ Affairs Division
- Consumer Affairs Division
- Private Schools Division
- Culture Promotion Division
Principal operations
Responsible for policies deeply related to the lives of the citizens of Tokyo, such as the following, and for the coordination and promotion of these programs across the bureaus.
- Public relations and public hearing activities
- Promotion of community activities and gender equality
- Intercultural policies
- Cultural affairs
- Private schools
- Consumer protection
Bureau of Tokyo 2020 Olympic and Paralympic Games Preparation
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- General Coordination Division
- Games Facilities Division
- Sports Promotion Division
Principal operations
Responsibilities include:
- Advancing consolidated efforts for the Tokyo 2020 Olympic and Paralympic games and the Rugby World Cup 2019 to ensure their success.
- Further promoting sports and advancing programs to achieve “Sports City Tokyo,” where the power of sports vitalizes both the city and its people
Bureau of Urban Development
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Urban Development Policy Division
- Housing Policy Promotion Division
- Urban Infrastructure Division
- Urban Development Projects Division
- Urban Building Division
- Metropolitan Housing Management Division
- US Military Facilities Relations Division
Principal operations
Responsible for tasks covering a broad range of fields including:
- Formulation of total urban development policies and housing policies
- Construction of roads, railways and other urban infrastructure
- Improvement of built-up areas through land readjustment and urban redevelopment projects
- Provision of guidance for housing land development and architectural structures
- Construction and management of metropolitan housing
- Measures for US military facilities
Bureau of Environment
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Climate Change & Energy Division
- Environmental Improvement Division
- Natural Environment Division
- Sustainable Materials Management Division
Principal operations
Undertakes measures to ensure a healthy and safe environment and to create a sustainable city including:
- Implementation of measures addressing climate change, electricity and energy issues, motor vehicle pollution, air, water and soil contamination, chemical substances, and wastes
- Preservation of the natural environment
- Assessment of environmental impact
- Environmental protection
Bureau of Social Welfare and Public Health
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Guidance and Inspection Division
- Medical Policy Division
- Health Policy Division
- Welfare Division
- Aging Population Programs Division
- Declining Birth Rate Countermeasures Division
- Disabled Persons Programs Division
- Health and Safety Division
Principal operations
Promotes integrated and comprehensive welfare, public health, and health care policies to meet the diverse needs of all Tokyo citizens so that they can live in their communities with a sense of reassurance. These include:
- Support for the disabled and citizens in all stages of life, from children to childrearing households and senior citizens
- Welfare benefits and measures for the homeless
- Promotion of an inclusive society
- Building of systems for delivery of health care
- Promotion of wellness
- Measures to address intractable diseases
- Provision of guidance to social welfare facilities and medical institutions, and their inspection
- Supervision and provision of guidance for food and medical items, and measures for environmental health and infectious diseases, in order to properly respond to health crises
Office of Metropolitan Hospital Management
Bureau/Division
- Management Planning Division
- Service Promotion Division
Principal operations
The office:
- Operates and manages eight metropolitan hospitals to quickly and accurately respond to the increasingly sophisticated and diversified medical needs of the residents
- Was established to allow metropolitan hospitals freedom in managing their own affairs
- Maintains close ties with metropolitan public health services and steadily promotes metropolitan hospital reform with the aim to enhance hospital services
- Has had the Tokyo Metropolitan Health and Medical Treatment Corporation, which manages local hospitals and institutions, under its jurisdiction since FY2006
Bureau of Industrial and Labor Affairs
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Commerce and Industry Division
- Financial Affairs Division
- Financial Supervision Division
- Tourism Division
- Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery Division
- Employment Division
Principal operations
Conducts programs to further strengthen and vitalize Tokyo’s industries, and other measures including:
- Provision of support to SMEs to, among others, improve and strengthen management, raise technological strength, promote entrepreneurship, vitalize shopping streets, and facilitate smoother fund procurement
- Promotion of the “Tokyo brand” to convey Tokyo’s attractions to the world
- Development of tourism resources and an environment to receive foreign visitors
- Development of the infrastructure and implementation of programs to raise successors for stable management of the agriculture, forestry, marine, and livestock industries
- Measures to secure food safety
- Promotion of a forestry cycle
- Registration and inspection/guidance for the money lending businesses
- Promotion of local employment
- Securing of proper labor environments
- Development and enhancement of working skills that match diverse needs
Central Wholesale Market
Bureau/Division
- Management Division
- Business Division
- New Market Development Division
Principal operations
To ensure that fresh food and items such as marine products, produce, meat, and flowers are quickly delivered to the consumers, as the establisher of 11 central wholesale markets in Tokyo, duties include:
- Guidance and supervision of trading based on the Wholesale Market Act and ordinances
- Maintenance and management of the market facilities
Facilities include:
- Tsukiji Market, Ota Market, and the Meat Market
Bureau of Construction
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Land Purchase Division
- Road and Street Administration Division
- Road and Street Construction Division
- Three Loop Roads Development Division
- Park Division
- River Division
Principal operations
Promotes the construction of urban infrastructure that will contribute to the creation of a sophisticated disaster-resilient city, with the aim to realize a comfortable, highly convenient, safe and attractive city, by implementing:
- Construction of the three loop roads and arterial roads of the capital region
- Upgrading of rivers to protect the city from floods
- Development of parks and other spaces that not only provide relaxing places for Tokyo’s residents, but serve as temporary refuge and bases for rescue efforts in the event of a disaster
- Construction and management of facilities such as zoos and aquariums for the enjoyment of the citizens
- Construction and management of cemeteries
- Implementation of proper maintenance and management and systematic renewals to ensure that the facilities are performing at their best
Bureau of Port and Harbor
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Port Management Division
- Waterfront Development Division
- Port Planning and Construction Division
- Island Harbors Division
Principal operations
Undertakes the:
- Development and promotion of the Port of Tokyo, which holds a crucial role as a major logistics hub supporting the National Capital Region
Other duties include:
- Development of landfi lls in the waterfront area and other areas
- Construction of waste treatment centers
- Work on marine park projects
- Implementation of disaster reduction measures for the Port of Tokyo and the upgrading of harbors, fishing ports, airports and coastline of the islands of Tokyo to protect the residents from tsunami, storm surges, and other flooding
Bureau of Accounting
Bureau/Division
- Management Division
- Police and Fire Department Cashier’s Division
Principal operations
As the organization in charge of accounting, activities include:
- Management and safeguarding of cash and securities
- Confirmation of obligations
- Preparation of annual financial statements
- Planning, guidance, and inspection of accounting activities
- Advancing accounting system reform through double entry accrual-based accounting
- Managing government funds
- Advancing PPP projects
- Providing supplies to each bureau
Tokyo Fire Department
Bureau/Division
- Planning and Coordination Division
- Administration Division
- Human Resources Division
- Fire Suppression Division
- Disaster Preparedness Division
- Emergency Medical Service Division
- Fire Prevention Division
- Equipment Division
- Fire Academy
- Fire Technology and Safety Laboratory
Principal operations
Pursuant to the Fire Organization Act, the department is established under the jurisdiction of the Governor of Tokyo for the special wards to work together in fulfilling their firefighting duties.
Pursuant to the Local Autonomy Law, nearly all of the municipalities in the Tama area entrust their administrative work to the metropolitan government.
Made up of headquarters, fire district headquarters, fire stations, fire station divisions, and fire station branches, the department protects the lives and assets of the Tokyo resident from disaster through:
- Prevention, vigilance, and suppression of fires
- Rescue at scenes of traffic accidents and other incidents and emergency medical services
- Implementation of disaster preparedness activities such as measures for earthquakes and floods
Public Enterprise Bureaus
Bureau of Transportation
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Personnel Division
- Property Administration Division
- Subway and Streetcar Service Division
- Bus Service Division
- Rolling Stock and Electricity Division
- Construction and Maintenance Division
Principal operations
- Operates the public transit systems of Toei Subway (Asakusa, Mita, Shinjuku, and Oedo lines), Toei Bus, Toei Streetcar, Nippori-Toneri Liner, and the Ueno Park Monorail, and provides safe and punctual services
- Undertakes the hydropower generation business using the Tamagawa River water system
Bureau of Waterworks
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Personnel Division
- Assets Management and Contracting Division
- Customer Service Division
- Purification Division
- Water Supply Division
- Construction Division
Tama Waterworks Reform Promotion Center
- Coordination Division
- Facilities Division
Principal operations
- Supplies water to the 13.04 million residents living in the ward area and the 26 municipalities of the Tama area, an area totaling about 1,239 km²
- As of the end of March 2015, the total volume of TMG’s water sources is 6.30 million m³/day, capacity of water purification facilities is 6.86 million m³/day, and total length of distribution pipes is 26,774 km
- Conducts the industrial-use water business that supplies industrial water to the eight wards along the Arakawa River and a portion of Nerima Ward
Bureau of Sewerage
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Personnel Division
- Accounting and Contracting Division
- Planning and Coordination Division
- Facilities Management and Maintenance Division
- Construction Division
Regional Sewerage Office
- Management Division
- Engineering Division
Principal operations
- Responsible for basic functions of the sewer system, i.e. sewage treatment, flood control through removal of rainwater, quality maintenance of public waters. In addition, based on the Management Plan 2016, formulated in February 2016, the following initiatives are promoted:
- Implementation of reconstruction of facilities, flood control, earthquake measures and other policies that help the residents of Tokyo feel safe and secure
- Combined sewer system improvement, advanced treatment, global warming measures, and other measures that contribute to the realization of a city with a good water environment and low environmental impact
- Stable provision of best services at minimum cost
Administrative Commissions
Board of Education (Office of Education)
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Division
- Metropolitan School Education Division
- Community Education Support Division
- Curriculum and Guidance Division
- Personnel Division
- Benefits and Welfare Division
Principal operations
- Made up of the Director General and five members appointed by the governor upon approval by the metropolitan assembly. The Director General serves a three-year term and the members serve a four-year term
- The Director-General shall preside over all affairs of the Board of Education and represents the Board.
Main administrative affairs include:
- Establishment and management of educational institutions such as public schools
- Personnel affairs such as appointment and dismissal of staff and teachers
- Admission, transfer, and withdrawal of students
- Provision of necessary directions, advice, and assistance to the municipal boards of education for the proper processing of affairs related to education
Secretariat to Election Administration Commission
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Section
- Election Section
Principal operations
- The Commission is made up of four members elected by the metropolitan assembly to a four-year term. In order to ensure fair elections, it is independent of the governor
- This collegiate administrative commission is assisted by the secretariat
Main duties include:
- Management of elections as stipulated under law
- Management of Supreme Court judge retention referendums
- Administrative work concerning election-related lawsuits
- Boosting public interest in elections
- Administrative work based on the Political Funds Control Act
Secretariat to Personnel Commission
Bureau/Division
- Personnel Management and Equity Division
- Civil Service Examiner’s Division
Principal operations
- The Secretariat assists the Commission, a specialized administrative institution for personnel affairs, which is independent of the appointing authority
- The Commission is made up of three members appointed by the governor for a four-year term upon approval by the metropolitan assembly
Principal powers of the Commission are:
- Establishment of proper employment conditions for metropolitan employees including their salaries and working hours
- Establishment of a neutral and fair appointment system (e.g.recruitment exams)
- Review and rendering of judgment on requests concerning staff employment conditions
- Fair review including rulings or decisions on appeals made by employees who were subject to adverse dispositions
Secretariat to Audit and Inspection Commissioners
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Section
- First, Second and Third Inspection Sections
- Technology Inspection Section
Principal operations
- The Secretariat assists the audit and inspection commissioners in implementing audits from the perspectives of compliance, economy, efficiency, and effectiveness
- Five commissioners (two metropolitan assembly members and three experts) are appointed by the governor upon approval by the metropolitan assembly
- They are commissioner entities established under the Local Autonomy Act to ensure fair and efficient administrative and fiscal operations by conducting audits and inspections on implementation of clerical work related to finances and control of projects related to management
Public Safety Commission (Metropolitan Police Department)
Bureau/Division
- Administration Bureau
- Personnel and Training Bureau
- Traffi c Bureau
- Security Bureau
- Community Police Affairs Bureau
- Public Security Bureau
- Criminal Investigation Bureau
- Community Safety Bureau
- Organized Crime Control Bureau
- Metropolitan Police Academy
- District Headquarters
- Crime Prevention Measures Task Force
- Victim Protection/Relief Task Force
- Olympic and Paralympic Games Task Force
Principal operations
- Commissions are established at the national and prefectural level as organizations to manage the police under the Police Act
- The Commission in Tokyo is placed under the jurisdiction of the governor
- Five members are appointed by the governor for a three-year term upon approval by the metropolitan assembly
Main powers vested under the Police Act and other laws and ordinances include:
- Management of the Metropolitan Police Department
- Issuance of driver licenses and traffi c control
- Designation of organized crime groups and revocation of designation
- Issuance, suspension, and revocation of business permits based on laws such as the Secondhand Articles Dealer Act and Pawnbroker Business Act
- Authorization of security services businesses
Secretariat to Labor Relations Commission
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Section
- Trial and Adjustment Section
Principal operations
- The Secretariat assists this collegiate administrative commission established under the Labor Union Act
- The Commission is made up of 39 members, with 13 each from public services, workers, and employers
The main purposes of the commission are:
- Stabilizing and normalizing labor relations such as settling disputes between labor unions and employers concerning labor conditions and union activity rules
- Helping workers subject to unfair labor practices
Secretariat to Expropriation Commission
Bureau/Division
- General Affairs Section
- Trial Section
Principal operations
- The Secretariat assists this collegiate organization, which is an administrative commission with quasi-judicial functions established under the stipulations of the Compulsory Purchase of Land Act
- The Commission promotes public interests and adjusts private assets concerning the use or expropriation of land and other properties necessary for projects in the public interest
- The seven committee members, as well as reserve members, are selected among those with abundant experience and knowledge on law, economy, or public administration, who can make fair judgments on public welfare
- The members are appointed by the governor to a three-year term upon approval by the metropolitan assembly
Legislative Organ
Secretariat to the Tokyo Metropolitan Assembly
Bureau/Division
- Management Division
- Procedures Division
- Research Division
Principal operations
- Supports the activities of the metropolitan assembly by assisting in the operation of plenary sessions and committee meetings
- Prepares the minutes of the meetings
- Prepares and conducts research for other materials necessary for activities of the assembly
- Carries out public relations for the assembly